转载声明:文章来源https://blog.csdn.net/wayne566/article/details/79106372
列举了二叉树的前序、中序、后序的递归和非递归遍历方法,以及层次遍历、分层输出的层次遍历方法。
举例如下: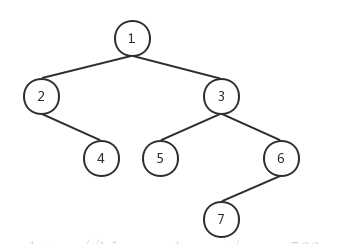
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//构造树结构测试用
TreeNode a = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode b = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode c = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode d = new TreeNode(4);
TreeNode e = new TreeNode(5);
TreeNode f = new TreeNode(6);
TreeNode g = new TreeNode(7);
a.left = b;
a.right = c;
b.right = d;
c.left = e;
c.right = f;
f.left = g;
System.out.print("recursivePreOrder: ");
recursivePreOrder(a);
System.out.print('\n' + "recursiveInOrder: ");
recursiveInOrder(a);
System.out.print('\n' + "recursivePostOrder: ");
recursivePostOrder(a);
System.out.print('\n' + "iterativePreOrder: ");
iterativePreOrder(a);
System.out.print('\n' + "iterativePreOrder_2: ");
iterativePreOrder_2(a);
System.out.print('\n' + "iterativeInOrder: ");
iterativeInOrder(a);
System.out.print('\n' + "iterativePostOrder: ");
iterativePostOrder(a);
System.out.print('\n' + "iterativePostOrder_2: ");
iterativePostOrder_2(a);
System.out.print('\n' + "iterativePostOrder_3: ");
iterativePostOrder_3(a);
System.out.print('\n' + "iterativeLevelOrder: ");
iterativeLevelOrder(a);
System.out.print('\n' + "iterativeLevelOrder_2: " + '\n');
iterativeLevelOrder_2(a);
System.out.print('\n' + "recursiveLevelOrder: ");
recurLevelOrder(a);
System.out.print('\n' + "recursiveLevelOrderBottom: " + '\n');
List<List<Integer>> lists = recursiveLevelOrderBottom(a);
for (List<Integer> list : lists) {
for (int p : list) {
System.out.print(p + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void visit(TreeNode p) {
System.out.print(p.val + " ");
}
//**********递归的先序遍历**********
public static void recursivePreOrder(TreeNode p) {
if (p == null) return;
visit(p);
recursivePreOrder(p.left);
recursivePreOrder(p.right);
}
//**********递归的中序遍历**********
public static void recursiveInOrder(TreeNode p) {
if (p == null) return;
recursiveInOrder(p.left);
visit(p);
recursiveInOrder(p.right);
}
//**********递归的后序遍历**********
public static void recursivePostOrder(TreeNode p) {
if (p == null) return;
recursivePostOrder(p.left);
recursivePostOrder(p.right);
visit(p);
}
//**********非递归的先序遍历**********
//手算的思想,先变访问边找,找到最左下方的,然后向上再向访问右边的
public static void iterativePreOrder(TreeNode p) {
if (p == null) return;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
while (!stack.empty() || p != null) {
while (p != null) {
visit(p);
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
}
p = stack.pop();
p = p.right;
}
}
//**********非递归的先序遍历**********
//栈的思想,按层次倒着进栈,利用后进先出解决顺序问题
public static void iterativePreOrder_2(TreeNode p) {
if (p == null) return;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
stack.push(p);
while (!stack.empty()) {
p = stack.pop();
visit(p);
if (p.right != null) stack.push(p.right);
if (p.left != null) stack.push(p.left);
}
}
//**********非递归的中序遍历**********
public static void iterativeInOrder(TreeNode p) {
if (p == null) return;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
while (!stack.empty() || p != null) {
while (p != null) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
}
p = stack.pop();
visit(p);
p = p.right;
}
}
//**********非递归的后序遍历**********
//注意prev的作用
public static void iterativePostOrder(TreeNode p) {
if (p == null) return;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode prev = p;
while (!stack.empty() || p != null) {
while (p != null) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
}
p = stack.peek().right;
if (p == null || p == prev) {
//若栈顶节点的右节点为空或者已经visit过,则按顺序应该访问栈顶节点
p = stack.pop();
visit(p);
//prev用来标记已经visit过这个节点
prev = p;
p = null;
}
}
}
//**********非递归的后序遍历**********
//和上一种方法思想类似
public static void iterativePostOrder_2(TreeNode p) {
if (p == null) return;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode prev = p;
while (p != null) {
while (p.left != null) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
}
while (p != null && (p.right == null || p.right == prev)) {
visit(p);
prev = p;
if (stack.empty()) return;
p = stack.pop();
}
stack.push(p);
p = p.right;
}
}
//**********非递归的后序遍历**********
//双栈法,易于理解
public static void iterativePostOrder_3(TreeNode p) {
if (p == null) return;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
Stack<TreeNode> result = new Stack<TreeNode>();
while (!stack.empty() || p != null) {
while (p != null) {
stack.push(p);
result.push(p);
p = p.right;
}
if (!stack.empty()) p = stack.pop().left;
}
while (!result.empty()) {
p = result.pop();
visit(p);
}
}
//**********非递归的层次遍历**********
public static void iterativeLevelOrder(TreeNode p) {
if (p == null) return;
LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(p);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
p = queue.poll();
if (p.left != null) queue.offer(p.left);
if (p.right != null) queue.offer(p.right);
visit(p);
}
}
//**********非递归的分层输出的层次遍历**********
public static void iterativeLevelOrder_1(TreeNode p) {
if (p == null) return;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(p);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int levelNum = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < levelNum; i++) {
p = queue.poll();
if (p.left != null) queue.offer(p.left);
if (p.right != null) queue.offer(p.right);
visit(p);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//**********非递归的分层输出的层次遍历**********
//维护两个int,代表上一层和下一层的节点数量,上一层遍历结束之后lineUp = lineDown; lineDown = 0;
public static void iterativeLevelOrder_2(TreeNode p) {
if (p == null) return;
LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
int lineUp = 1, lineDown = 0;
queue.offer(p);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
p = queue.poll();
visit(p);
if (p.left != null){
queue.offer(p.left);
lineDown++;
}
if (p.right != null){
queue.offer(p.right);
lineDown++;
}
if (--lineUp == 0) {
lineUp = lineDown;
lineDown = 0;
System.out.println();
}
}
}
//**********递归的层次遍历访问**********
public static void recurLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
int depth = maxDepth(root);
//如果要倒序访问只需修改此处顺序
for (int i = 1; i <= depth; i++) visitNodeAtDepth(root, i);
}
//访问特定层的节点
public static void visitNodeAtDepth(TreeNode p, int depth) {
if (p == null || depth < 1) return;
//因为要按顺序访问(打印),所以要规定必须到某一层才能visit
if (depth == 1) {
visit(p);
return;
}
//每次都要遍历depth之上的所有层
visitNodeAtDepth(p.left, depth - 1);
visitNodeAtDepth(p.right, depth - 1);
}
//得到树的层数
public static int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
//**********递归的倒序层次遍历并保存结果至list**********
//LeetCode107
//之所以用LinkedList是因为有addFirst()方法,可以逆序保存
public static List<List<Integer>> recursiveLevelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
LinkedList<List<Integer>> lists = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
addToList(lists, root, 1);
return lists;
}
//将depth层的p节点保存至list
public static void addToList(LinkedList<List<Integer>> lists, TreeNode p, int depth) {
if (p == null) return;
if (lists.size() < depth) lists.addFirst(new LinkedList<Integer>());
//由于不用输出只是保存,可以使用get控制保存在哪一层,所以不用规定层数
lists.get(lists.size() - depth).add(p.val);
addToList(lists, p.left, depth + 1);
addToList(lists, p.right, depth + 1);
}
}运行结果:
recursivePreOrder: 1 2 4 3 5 6 7
recursiveInOrder: 2 4 1 5 3 7 6
recursivePostOrder: 4 2 5 7 6 3 1
iterativePreOrder: 1 2 4 3 5 6 7
iterativePreOrder_2: 1 2 4 3 5 6 7
iterativeInOrder: 2 4 1 5 3 7 6
iterativePostOrder: 4 2 5 7 6 3 1
iterativePostOrder_2: 4 2 5 7 6 3 1
iterativePostOrder_3: 4 2 5 7 6 3 1
iterativeLevelOrder: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
iterativeLevelOrder_2:
1
2 3
4 5 6
7
recursiveLevelOrder: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
recursiveLevelOrderBottom:
7
4 5 6
2 3
1


看完解析才知道应该是这样的思路
简直是我梦想中的offer,好想去上班